
The mining of coal, metals, and other minerals causes loss of natural habitats across the entire globe. However, available data is insufficient to measure the extent of these impacts. IIASA alumnus Victor Maus and his colleagues mapped more than 57,000 km² of mining areas over the whole world using satellite images.
 © IIASA
© IIASA
Using these data, we can improve the calculation of environmental indicators of global mineral extraction and thus support the development of less harmful ways to extract natural resources. Further, linking these impacts to supply chains can help to answer questions related to our consumption of goods. For example, which impacts the extraction of minerals used in our smartphones cases and where on the planet they occur? We hope that many others will use the mining areas data for their own research and applications. Therefore, the data is fully open to everyone. You can explore the global mining areas using our visualization tool at www.fineprint.global/viewer or you can download the full data set from doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.910894. The complete description of the data and methods is in our paper available from www.nature.com/articles/s41597-020-00624-w.
This blog post first appeared on the Springer Nature “Behind the paper” website. Read the original post here.
Note: This article gives the views of the authors, and not the position of the Nexus blog, nor of the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis.
Our modern lifestyles and consumption patterns cause environmental and social impacts geographically displaced in production sites thousands of kilometres away from where the raw materials are extracted. Complex supply chains connecting mineral mining regions to consumers often obscure these impacts. Our team at the Vienna University of Economics and Business is investigating these connections and associated impacts on a global-scale www.fineprint.global.
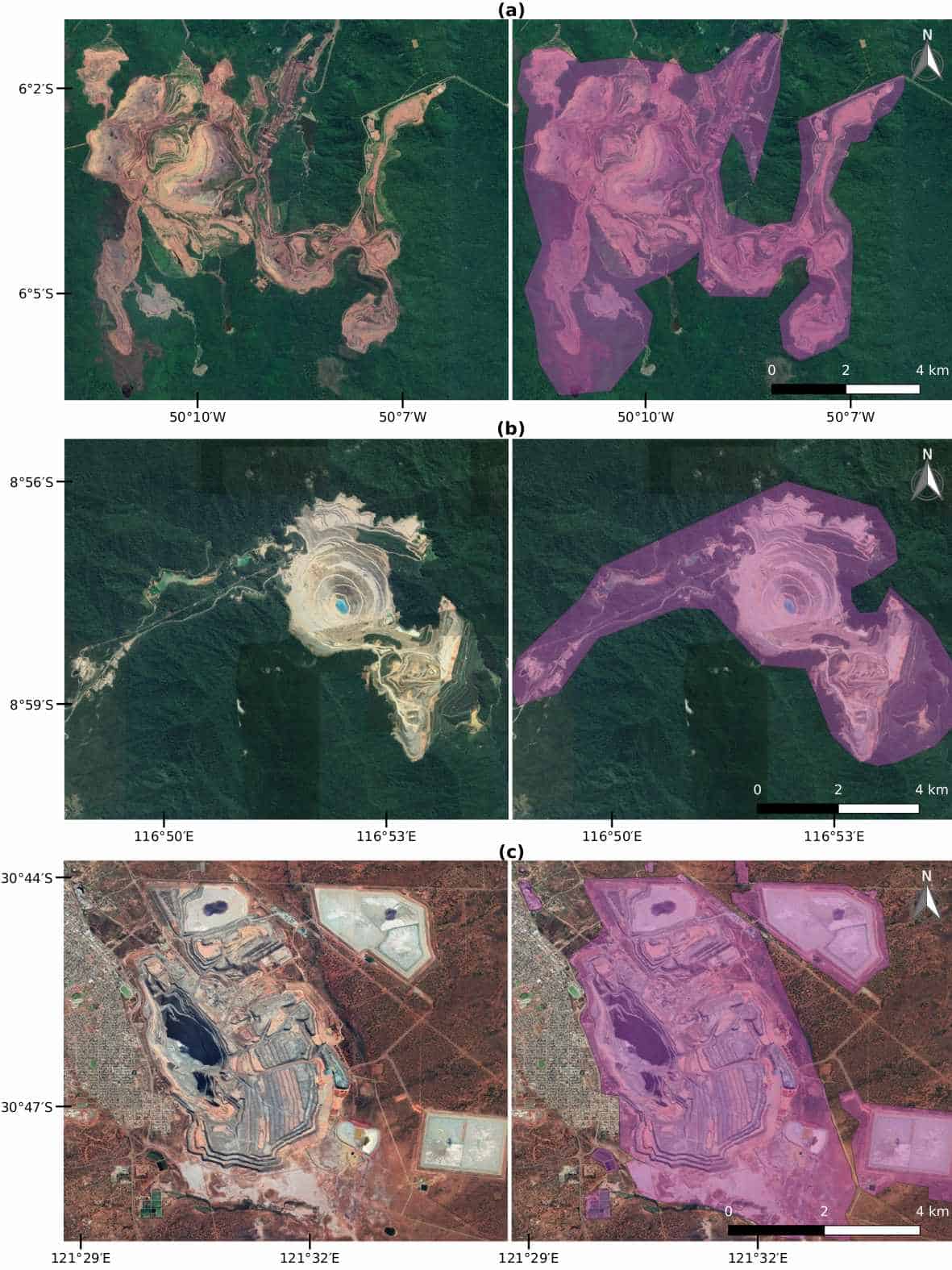
However, some mining impacts are not well documented across the globe, for example, where and how much area is used to extract metals, coal, and other essential minerals are unknown. This information is necessary to assess the environmental implications, such as forest and biodiversity loss associated with mining activities. To cover this data gap, we analyzed the satellite images of more than 6,000 known mining regions all around the world.
Visually identifying such a large number of mines in these images is not an easy task. Imagine you are flying and watching from the window of a plane, how many objects on the Earth’s surface can you identify and how fast? Using satellite images, we searched and mapped mines over the whole globe. It was a very time-consuming and exhausting task, but we also learned a lot about what is happening on the ground. Besides, it was very interesting to virtually visit a vast range of mining places across the globe and realize the large variety of ecosystems that are affected by our increasing demand for nature’s resources.
The result of our adventure is a global data set covering more than 21,000 mapped areas adding up to around 57,000 km² (that is about the size of Croatia or Togo). These mapped areas cover open cuts, tailings dams, piles of rocks, buildings, and other infrastructures related to the mining activities — some of them extending to almost 10 km (see figure below). We also learned that around 50 % of the mapped mining area is concentrated in only five countries, China, Australia, the United States, Russia, and Chile.