
Using a novel modeling approach, new research published in Nature Ecology and Evolution reveals the location and intensity of key threats to biodiversity on land and identifies priority areas across the world to help inform conservation decision making at national and local levels.
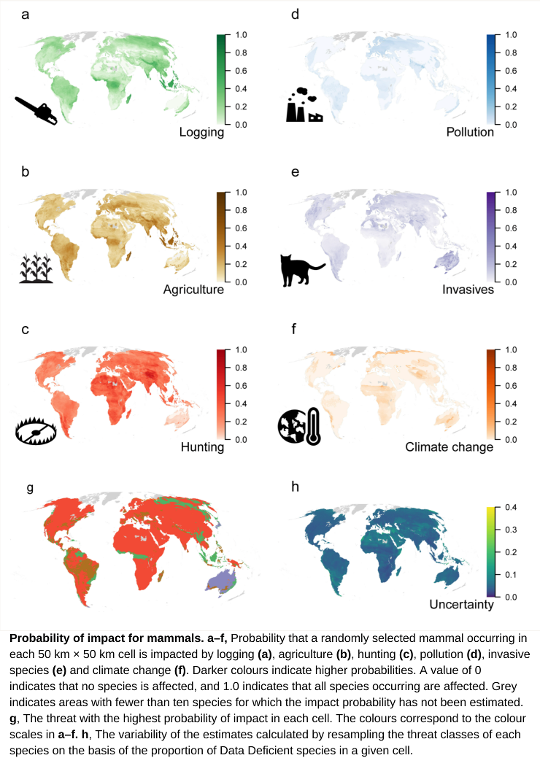
IIASA scientists are part of a team of leading researchers who have produced global maps for the six main threats affecting terrestrial amphibians, birds, and mammals: agriculture, hunting and trapping, logging, pollution, invasive species, and climate change. Results show that agriculture and logging are pervasive in the tropics and that hunting and trapping is the most geographically widespread threat to mammals and birds. There are sizeable continental areas in which there is more than a 50% chance that any particular amphibian, mammal, or bird species is threatened by logging, hunting and trapping, agriculture, invasive species, or climate change.
The world is facing a global nature crisis, yet information about the location and intensity of the threats responsible for biodiversity loss remains limited. Information on the spatial intensity of threats and how they affect species on the ground is critically important to improving and targeting conservation responses. This study presents both a first attempt to map this information and a research track to improve our understanding of how threats to biodiversity vary across the world.
Using the IUCN Red List to map threats to terrestrial vertebrates on a global scale identifies the most prevalent threat for each taxa. It finds that agriculture is the greatest threat to amphibians, being the most prevalent threat to these species across 44% of global lands. For birds and mammals, hunting and trapping is most prevalent, ranking as the highest threat across 50% of land for birds and 73% of land for mammals. Agriculture is the most prevalent threat for amphibians, mammals, and birds combined.
The research also identifies locations where threats are particularly prevalent. In Southeast Asia, particularly the islands of Sumatra and Borneo, as well as Madagascar, there is a high risk of impact from all six threats to amphibians, birds, and mammals. For amphibians, Europe stood out as a region of high threat impact due to a combination of agriculture, invasive species and pollution. Polar regions, the east coast of Australia and South Africa are mostly likely to be impacted by climate change, affecting birds in particular.
Mike Harfoot, one of the two lead authors of the paper from the UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC), says: “We are facing a global nature crisis and the next ten years is a crucial window for taking decisive action to tackle biodiversity loss. Our results reveal the location and intensity of human-caused threats to nature. This information can support decision makers at a range of levels in identifying where action to reduce these threats could yield the best results for people and planet. With further work, we will improve this information in terms of accuracy and the breadth of nature considered.”
To help guide conservation action, the authors also combined threat impact data with spatial information on biodiversity importance to create conservation risk maps that identify high priority areas for threat mitigation. These maps are one tool that can support and inform decision making on national and other levels as appropriate. The areas identified include the Himalayas, Southeast Asia, the east coast of Australia, the dry forest of Madagascar, the Albertine Rift and East Arc Mountains in eastern Africa, the Guinean forests of West Africa, the Atlantic Forest, the Amazon basin and the Northern Andes into Panama and Costa Rica in South and Central America.
Jonas Geldmann, Assistant Professor at the Center for Macroecology, Evolution and Climate of the University of Copenhagen, and co-lead author of this paper says: “These maps also reveal that priority areas for one threat rarely overlap with that of other threats, meaning that to effectively respond to the current human impact on biodiversity we need a global response.”
Piero Visconti, a study co-author who leads the IIASA Biodiversity, Ecology, and Conservation Research Group, says: "Despite ubiquitous sensors and advanced technology, we still know so little about the exact location and intensity of some of the most important threats to species such as hunting and trapping and the presence of invasive species. On-the-ground surveys are irreplaceable to have an accurate local picture of the distribution and impacts of these threats, but they are challenging and resource intensive, and therefore difficult to do at the scale at which some conservation decisions are made. This analysis is an important first step that can help efficiently direct local assessments of specific threats to terrestrial biodiversity, and start identifying the most appropriate local solutions."
In 2022, the Conference of the Parties to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity will meet in Kunming, China, and is expected to adopt a post-2020 global biodiversity framework, a new global plan for nature. The research released today helps to demonstrate the various types and geographic breadth of the threats to terrestrial species, and so the scale of the challenge for transformation that the framework must deliver if we are to conserve life on Earth.
 © Harfoot
© Harfoot
Harfoot et al., (2021) Using the IUCN Red List to map threats to terrestrial vertebrates at global scale, Nature Ecology and Evolution. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-021- 01542-9
Reference:
Harfoot, M.B.J., Johnston, A., Balmford, A., Burgess, N.D., Butchart, S.H.M., Dias, M.P., Hazin, C., Hilton-Taylor, C., et al. (2021). Using the IUCN Red List to map threats to terrestrial vertebrates at global scale. Nature Ecology & Evolution DOI: 10.1038/s41559-021-01542-9 [pure.iiasa.ac.at/17397]
News

28 June 2024
Drowning in waste: pollution hotspots in aquatic environments

27 June 2024
What can social media tell us about public views on climate change?

21 June 2024

