A new study finds that standalone solar photovoltaic irrigation systems have the potential to meet more than a third of the water needs for crops in small-scale farms across sub-Saharan Africa.
In sub-Saharan Africa 80% of agricultural production is from smallholder farmers, who face constraints on increasing farm productivity resulting in a large yield gap. Extensive rain-fed agriculture (90% of all cropland) under unpredictable and erratic rainfall pattern is a leading cause of the low productivity and food insecurity in Africa, together with a low degree of mechanization. This has been reinforcing a persistent poverty trap, triggered by cyclical famines that are jeopardizing local development opportunities.
In a new IIASA-led study, published in Environmental Research Letters, as part of the research project Renewables for African Agriculture (RE4AFAGRI), an international team of researchers developed an open-source modeling framework that used various datasets related to agriculture, water, energy, expenses, and infrastructure. This framework was employed to calculate local irrigation needs, determine the necessary size and cost of technology components like water pumps, solar PV modules, batteries, and irrigation systems, and assess the economic prospects and sustainable development impacts of adopting solar pumps.
“We estimate an average discounted investment requirement of USD 3 billion per year, generating potential profits of over USD 5 billion per year from increased yields to smallholder farmers, as well as significant food security and energy access co-benefits,” explains Giacomo Falchetta, lead author of the study and a researcher in the Integrated Assessment and Climate Change Research Group of the IIASA Energy, Climate, and Environment Program. “Reducing the irrigation gap with cost-effective solar pumps can boost food production and improve nutrition, contributing to SDG 2 (Zero Hunger). Furthermore, surplus electricity generated by these systems could serve other energy needs, aligning with SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy).”
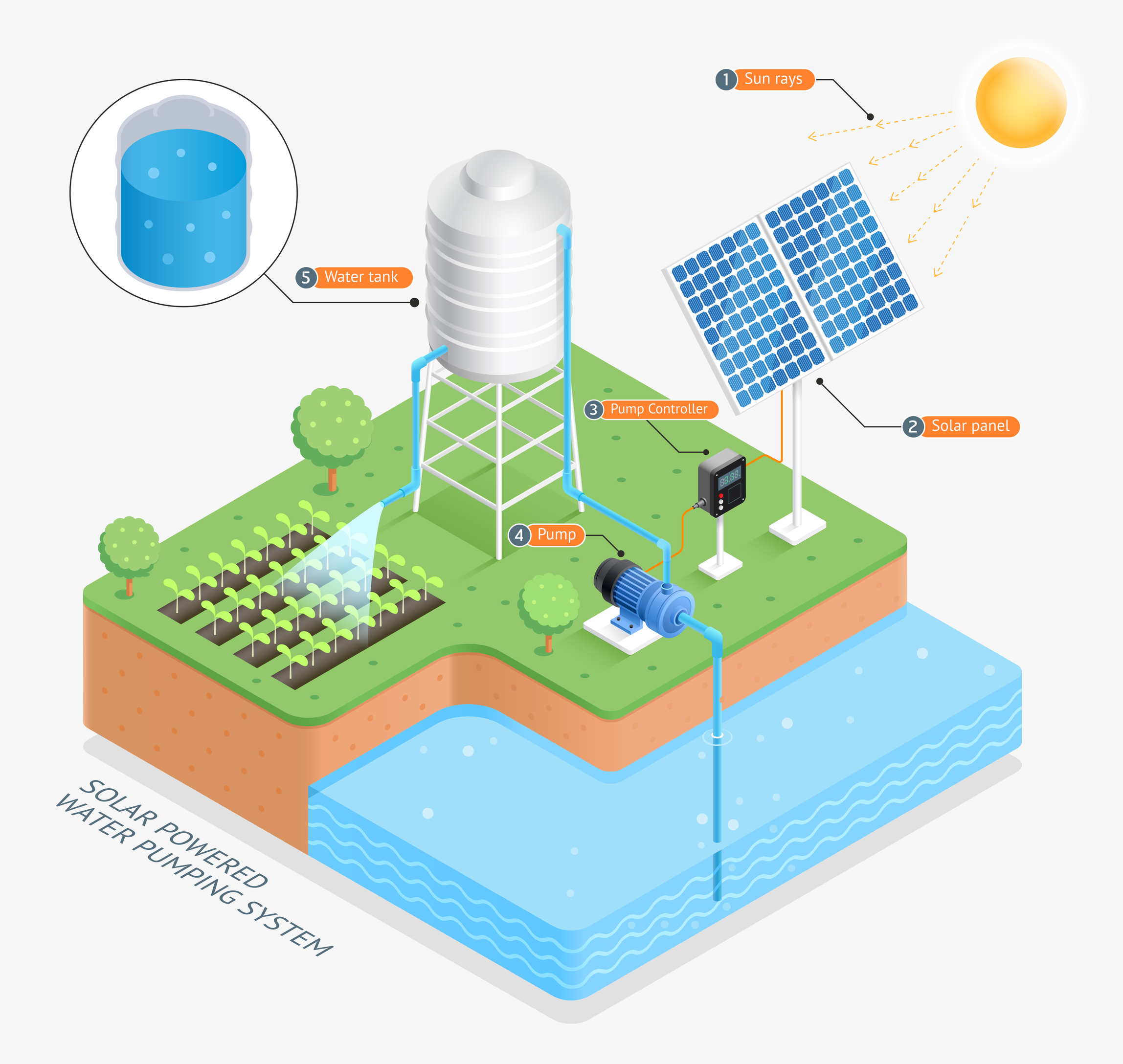
Solar powered water pumping system
Crucially, the authors of the study demonstrate the great importance of business models and investment incentives, crop prices, and PV and battery costs, in shaping the economic feasibility and profitability of solar irrigation.
“Using a business model that spreads out all initial expenses more than doubles the number of workable solar irrigation systems, presenting a huge potential to achieving the SDGs in the process,” notes IIASA Transformative Institutional and Social Solutions Research Group Leader Shonali Pachauri. “On the other hand, the study highlights that without strong land and water resource management infrastructure and governance, a widespread deployment of solar pumps may drive an unsustainable exploitation of water sources and reduce environmental flows. Consequently, both investing in infrastructure, such as reservoirs for water management during seasonal variations, and enhancing water resource governance, are critical factors for ensuring the sustainability of widespread solar pump deployment.”
The analysis and the novel open-source modeling framework can support public and private actors working along the water-energy-food-economy nexus in identifying economically feasible areas and quantifying the potential net economic benefit of developing solar irrigation, and can thus foster investment in the sector.
The RE4AFAGRI project is part of the Long-Term Joint European Union – African Union Research and Innovation Partnership on Renewable Energy (LEAP-RE) initiative.
Reference
Falchetta, G., Semeria, F., Tuninetti, M., Giordano, V., Pachauri, S., Byers, E. (2023). Solar irrigation in sub-Saharan Africa: economic feasibility and development potential. Environmental Research Letters. DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/acefe5
News

22 July 2024
Are sustainable aviation fuels truly sustainable?

17 July 2024
Forests endure as carbon sink despite regional pressures

16 July 2024