In recent decades, fertility rates in high-income countries have steadily declined. A new study analyzed demographic trends, patterns, determinants, and consequences. The authors emphasize that despite the significant economic challenges posed by low fertility, a strategic and consistent policy response can effectively mitigate most adverse consequences.
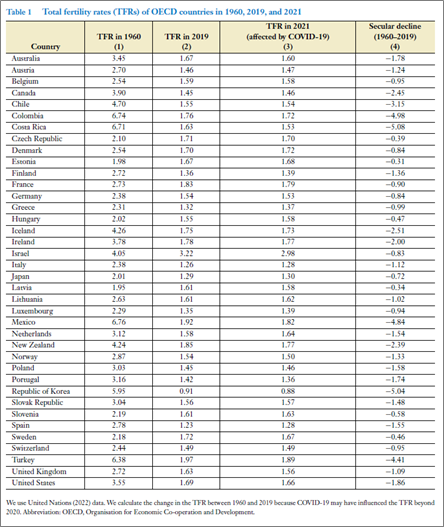
Across all 38 Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Member countries – spanning from North and South America to Europe and Asia-Pacific – the total fertility rate, which indicates the average number of children a woman is expected to have based on current age-specific fertility rates, has fallen. With the exception of Israel, the total fertility rate in 2019 is below the replacement rate of 2.1 children per woman.
Below-replacement fertility, leading to a shrinking population, is also a major issue for China, where the total fertility rate was 1.50 in 2019. It is also expected to become significant for India, other South and Southeast Asian countries, and many Latin American countries.
“Low fertility and its economic challenges will become a global trend in the coming years. While ecologically beneficial, shrinking populations raise concerns about sustaining economic growth and social security. Some policy discussions on this topic are confused and exaggerated – our analysis aims to clarify the debate by compiling recent research and evidence,” explains study coauthor Michael Kuhn, IIASA Economic Frontiers Program Director.
The study, published in Annual Review of Economics, shows that fertility decline can be attributed to a variety of factors. These include income and educational growth, shifts in social norms and behaviors, the evolution of family roles away from traditional insurance mechanisms for old age, and the uncertainties of a complex modern world. Biological factors may also play a role: recent research shows that over the past 50 years, human sperm counts appear to have fallen by more than 50% around the globe. These drivers often interact, and their impact varies greatly depending on the context. This variability suggests that in different regions, these factors may influence fertility trends differently or even in opposing directions.
“One insight that becomes evident from compiling diverse fertility research is that fertility is influenced by a mix of biological, social, economic, and behavioral factors, shaped by uncertainty and emotions. While fertility decline poses economic challenges rather than environmental ones, economic systems can adjust to these changes through robust and thoughtful policies,” notes Kuhn.
For example, expanding education helps stabilize the economy by boosting productivity through skilled workers and fostering innovation. Additionally, lower fertility often results in increased savings, allowing for investment in capital and automation technologies like robots to offset the declining workforce.
Given the complexity of fertility, attempting to directly "stir" or "stimulate" it through targeted policy initiatives may seem challenging or even impractical. Instead, it is crucial to design economies that allow individuals to freely choose their fertility based on preferences rather than constraints. This involves creating nurturing environments where children can thrive in a sustainable world focused on wellbeing, rather than solely on economic performance. It also means fostering socially responsible individuals and adapting economic systems to accommodate long-term demographic changes.
The authors emphasize that the decline in fertility, coupled with population aging and potential depopulation, should not serve as excuses to delay urgent climate and environmental transitions; instead, they should be addressed through decisive and coherent policymaking.
Reference
Bloom, David E., Kuhn, M., Prettner, K. (2024). Fertility in High-Income Countries: Trends, Patterns, Determinants, and Consequences. Annual Review of Economics DOI: 10.1146/annurev-economics-081523-013750
News

22 August 2024
Meeting ambitious restoration targets in Brazil’s Atlantic Forest

14 August 2024
Exploring options for the sustainable management of phosphorus

12 August 2024